Theme: Acquainting New Insights of Diabetes and Healthcare
Diabetic 2018
ME Conferences takes the immense pleasure of inviting the scientists, physicians, endocrinologists, physicians and scholars to the ‘’26th International Diabetes and Healthcare conference ‘’ on November 26th and 27th at Helsinki, Finland. The Annual conference enlightens the recent advancements related to Diabetes and aims at sharing the knowledge of the expertise in this field where the new generation scholars and researchers can increase their knowledge related to diabetes. The scientific sessions include the various sessions which emphasize on Consequences of Diabetes in Human, Cellular and Molecular Endocrinology, Hypertension and Diabetes, Neurologic problems and Diabetes, Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetes, Endocrine Complications of Diabetes, Treatment of Diabetes and Diabetes in Healthcare.
ME Conferences welcome the delegates across the country to enlighten the young and fresh minds of the scholars, researchers, student communities and industrial delegates to attend the ‘’26th International Diabetes and Healthcare Conference’’ as it is open to research methodologies which explores the new dimensions regarding this field.
Why to attend?
This conference will provide the focused learning on the distribution of knowledge, opportunities to network and discuss science and medicine on diabetes and healthcare and the recent advances and technologies related Diabetes for the making of better health. Fresh minds will have the opportunity to explore more areas of expertise on Healthcare in Diabetes. With members from all around the world increasing the knowledge about Diabetes and Healthcare and the increase in the new advance related to Diabetes, this is your best chance to reach the largest gathering of participants from Diabetes Community.
Target Audiences:
- Diabetologists
- Researchers
- Endocrinologists
- Doctors
- Physicians
- Nutritionists
- Scientists
- Academic Professionals
- Medical Colleges and Pharma Companies
- Medical Hospitals
- Students
- Business Entrepreneurs
- Manufacture Medical Devices & Companies
- Healthcare Training Institute
- Oncologists
- Neurologists
- Pediatric doctors
- Fitness Professionals
- Public Health Professionals
Track: Recent Advancement in Diabetes
Although Diabetes has been known since antiquity, treatments have been known thoroughly since the 21st century. The selection and application of a glucose-lowering therapy are dependent on many considerations like body mass index, ability to self-monitor the glucose level are the recent advances in Diabetes. The drugs used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes poses limitations, they have side-effects. The other medications strategies constitute a combination of therapy of insulin with sulfonylureas which reduces the daily requirement of insulin and insulin - metformin combination therapy. Drug-induced diabetes insipidus is always unresponsiveness of the kidneys to the action of antidiuretic hormone A variety of medications have been associated with the development of diabetes. Medicines which are used to treat obesity are proving to have significant health benefits for patients with type 2 diabetes. Pancreas and islet cell transplantation is the subject of ongoing research. There is much hope that new treatments outlined in this review will result in improved outcomes in the treatment of diabetes. Nanotechnology has a great deal for the world of medicines in diabetes.
Track: Diabetes and Nutrition
Nutrition plays a leading role in treating the patients with Diabetes. Eating well in a balanced manner can control the blood sugar of a patient. Medical nutrition therapy is an important topic of diabetes management and self-management of diabetes education. Macronutrients are the key diet of nutrition for the patients. Medical nutrition therapy has certain goals for the patients.
In recent years, diabetologists have considered that a little amount of sugar does not harm the sugar level of the patients. Patients suffering from type-1 and type -2 diabetes have to intake different nutritional diets to maintain their health. Low carb diets are generally preferred for the type-1 diabetic patients.
Track: Diabetes and Cancer
Studies for the association of cancer and diabetes have been conducted over a period of years. Both the diseases are very complex, and they are distinguished very categorically. Cancers that generally occur in the Diabetic patients are liver, pancreas, and bladder.
Worldwide cancer is the 2nd while Diabetes is the 12th leading cause of death in humans. In the U. S, the prevalence of diabetes in the year 2015 was10.5%.Results of some studies suggest that diabetes may increase the mortality of patients suffering from cancer. Modifiable and non-modifiable (potential) risk factors are common in both cancer and diabetes patients which includes aging, obesity, sex, diet, alcohol, and smoking.
Track: Genetic Diabetes
Diabetes, regularly alluded as diabetes mellitus, depicts a gathering of metabolic maladies is either on the grounds that insulin creation is insufficient, or in light of the fact that the body's phones don't react appropriately to insulin, or both the sorts. In type-1 diabetic patients, they inherit risk factors from both parents. Recent research has shown that offspring develop 3%of the time if the mother has the condition and 5% if the father has the condition. Environmental changes also trigger type-1 diabetes. Several viruses also trigger type-1 diabetes like measles virus, rotavirus.
Type-2 is the more generic form of disorder which includes 90% of the world cases. 70% patients with type-2 diabetes are inherited from the parents whereas the remaining patients were obese.
Track: Diabetes and Immunology
Type 1 diabetes is characterized by an absolute loss of insulin secretion. It results from an autoimmune process that destroys insulin-producing β cells within the pancreatic islet. The importance of genetic factors in the etiology of type 1 diabetes is demonstrated by agreement rates of 5–10% in dizygotic twins and up to 27% in monozygotic twins. Patients with type 1 diabetes are at increased risk of other immune-mediated diseases like thyroid disease, coeliac disease, autoimmune gastritis and Addison's disease.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is characterized by impaired insulin secretion, glucose intolerance, and hyperglycemia. Inflammation is considered as a major driving force in type -2 diabetes and associated complications also arise along with it. Components of the immune system are altered in obesity and type 2 diabetes with the most changes occurring in adipose tissue, the liver, pancreatic islets, the vasculature and circulating leukocytes.
Track: Biomarkers for Diabetes
“Biomarker”, are called “molecular marker” or a “signature molecule”. These viewed as direct or indirect markers of the extent of disease as they lay outside in a casual way. HbA1c is considered a biomarker for a risk factor that is for retinopathy, nephropathy and other vascular diseases. Biomarkers enable preventive measures to be applied at the subclinical stage and the responses to preventive or therapeutic measures to be monitored. Cases over the past two decades have yielded sample sets, mostly blood products and urine from a large category of patients with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Track: Cellular and Molecular Endocrinology
The Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology addresses the molecular and cell biology of endocrine organs and their products. Functional analysis of genomic, epigenomic and proteomic patterns of hormone action plays a significant role in the molecular endocrinology. Subjects related to biochemical and molecular aspects of endocrine research and cell regulation include hormone-regulated gene expression, structure and physicochemical properties of hormones, hormone receptors and other hormone-binding components, synthesis, secretion, metabolism and inactivation of hormones, neurotransmitters, hormonal control of differentiation, related control mechanisms in non-mammalian systems.
Track: Case Studies and New Research Advances in Diabetes
The main aim of the diabetes is to detect the overall condition of the disorder, there are numerous case and research studies including animal models and human models. Type 2 diabetes is a modern epidemic. The aim of the ongoing research is to re-investigate the mechanisms by which and the depth in which integrated care for diabetes has been implemented, whose outcomes have been achieved and how the context and mechanisms have affected the outcomes. Two distinct types of prediabetes, depending on when the body fails to produce insulin, the hormone that signals body tissues to use glucose: impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose. Scientists are analyzing the data to understand the effects of different drugs on the two distinct types of prediabetes.
Track: Consequences of Diabetes in Human
Diabetes affects long-term damage to our body. Diabetic complications take a few years of poorly controlled diabetes to develop and these can be prevented by maintaining a strong level of control on diabetes, blood pressure, blood sugar level and cholesterol. Diabetes and coronary heart disease are closely related. Diabetes contributes to high blood pressure and relates to high cholesterol. The presence of nerve damage (neuropathy) is commonly noticed by numbness or tingling sensation in the hands or feet, lack of arousal in the penis or clitoris, excessive sweating. Unmanaged diabetes can also lead to skin conditions like the eruption of xanthomatotic, which causes hard yellow bumps with a red ring, digital sclerosis, which results in thick skin often on the hands or feet, diabetic dermopathy, which causes brown patches on the skin.
Track: Hypertension and Diabetes
Hypertension is a greatly regular condition in diabetes, influencing close around 20– 60% of patients with diabetes. In type 1 diabetes, hypertension mirrors the beginning of diabetic nephropathy which builds the danger of both full scale vascular and smaller scale vascular confusions. Uncontrolled diabetes expands the hazard for hypertension. Insulin protections type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia and focal heftiness have been archived in a few populaces. Other conceivable reasons for hypertension with diabetes and insulin protection/ hyperinsulinemia incorporate actuation of the thoughtful sensory system, expanded renal tubular sodium maintenance, raised intracellular calcium focus and vascular smooth muscle cell multiplication and atherosclerosis.
Track: Neurologic problems and Diabetes
Diabetic neuropathy is a group of nerve issue caused by diabetes. The fringe nerves, autonomic nerves, cranial nerves, spinal string, and mind are for the most part associated with diabetes. Diabetic neuropathies additionally give off an impression of being particularly regular in individuals who have issues controlling their blood glucose, likewise called glucose, and additionally those with elevated amounts of blood fat and circulatory strain and the individuals who are large. Side effects of nerve harm, for the most part, incorporate deadness, shivering, or agony in the toes, feet, legs, hands, arms, and fingers, acid reflux, sickness, or spewing, looseness of the bowels or blockage. Some hereditary issue related to diabetes incorporates mitochondrial disorder, wolfram disorder and many more.
Track: Diabetes and Treatment
Diabetes is a typical ailment, yet every individual needs interesting consideration. A fasting glucose test, an oral glucose resistance test (OGTT), The A1C test are three of the most widely recognized tests for the preparatory trial of Diabetes. Research on Insulin is widely examined in National Diabetes Conference and Diabetes affiliations. Present day disclosures have the ability to help individuals living with type 1 or type 2 diabetes and treated with insulin to achieve the fantasy of perfect control of glucose. Eating an adjusted eating regimen is fundamental for individuals who have diabetes, so working up with the specialist; dietician or nutritionist likewise assumes a noteworthy part in the control of diabetes.
Track: Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy, likewise called diabetic eye malady, is a medicinal condition in which causes harm in the retina because of diabetes mellitus and is a reason for visual impairment. Diabetic macular edema (DME) is an outcome of diabetic retinopathy, which causes swelling in a zone of the retina called the macula. Beginning times of diabetic retinopathy, as a rule, have no manifestations. The regular side effects of retinopathy incorporate sudden changes in vision/obscured vision, eye floaters, and spots, twofold vision, eye torment. Diabetic retinopathy is recognized amid an eye examination that incorporates visual keenness test, Fundus Fluorescence angiography (FFA), and Optical soundness tomography (OCT). The NEI is directing and supporting exploration that looks for better approaches to recognize, treat, and avert vision misfortune in individuals with diabetes.
Track: Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetes
Undifferentiated organism treatment holds massive guarantee for the treatment of patients with diabetes mellitus. The expanding weight of diabetes worldwide is notable, and the impacts on medicinal services costs and inhuman enduring, dismalness, and mortality will be fundamentally felt in the creating countries including India, China, and nations in Africa. Foundational microorganisms hold colossal potential as a wellspring of insulin-delivering cells that could be put in protection since undeveloped cells can possibly turn out to be for all intents and purposes any sort of cell. Grown-up immature microorganisms, undifferentiated and versatile, can change into the cells of innumerable organs and structures inside the human body. Undifferentiated organism treatment for diabetes type 2 enables the body's normal mending procedure to work quicker and all the more adequately. These progressions in the treatment of type 2 diabetes work to completely recover absent or harmed tissue that the body would not conventionally regrow. As per the International Diabetes Federation, diabetes as of now influences 7% of the total populace — about 250 million people around the world. This aggregate is relied upon to ascend to 380 million by 2025 because of maturing populaces, evolving ways of life, and a current overall increment in corpulence.
Track: Diabetes in Healthcare
Social insurance change calls for new ways to deal with diabetes mind conveyance and more noteworthy accentuation on averting diabetes and its intricacy. Medicinal services are the upkeep or change of wellbeing by means of the avoidance, analysis, and treatment of malady, sickness, damage, and other physical and mental hindrances in people. Social insurance is conveyed by wellbeing experts (suppliers or professionals) in unified wellbeing callings, doctors, doctor partners, dentistry, maternity care, nursing, pharmaceutical, optometry, audiology, drug store, brain science, and other wellbeing callings. Essential care is frequently utilized as the term for the social insurance administrations which assume a part of the nearby group. It can be given in various settings. Secondary care incorporates intense care: fundamental treatment for a brief timeframe for a brief yet genuine sickness, damage or other wellbeing condition, for example, in a doctor's facility crisis division. It likewise incorporates gifted participation amid labor, escalated care, and medicinal imaging administrations. There is colossal vitality around new advancement and new businesses endeavoring to take care of different issues in the medicinal services framework. Diabetes mind has gradually been developing from a supplier overwhelmed way to deal with a cooperative exertion between the human services supplier and patient.
Track: Clinical Informatics
Clinical Informatics is an integrated way to improving patient care, advancing medicine and managing the health system through the use of clinical and technical knowledge combined with leadership and management skills. This helps to ensure adequate and qualified support of clinician objectives and industry best practices.
Track: Endocrine Complications of Diabetes
Diabetic confusions give off an impression of being multifactorial in beginning, yet specifically, the biochemical procedure of cutting-edge glycation, which is quickened in diabetes because of incessant hyperglycemia and expanded oxidative pressure, has been hypothesized to assume a focal part in the endocrine issue. The endocrine issue is regularly very unpredictable, including a blended picture of hypo emission and hyper discharge as a result of the criticism instruments engaged with the endocrine framework. Endocrinology focuses generally on the endocrine organs or those organs that may realize hormone awkwardness. These organs fuse the pituitary, thyroid, adrenals, ovaries, gonads, and pancreas. This can be a convoluted specialty. There are various organs and hormones in the body, each with their own specific occupations to do. It is a delicate compound modify that keeps our bodies running effectively with alongside no effort on our part. Patients with diabetes mellitus have an expanded danger of building up some rheumatologic ailments, including muscle localized necrosis, carpal passage syndrome, etc.
Track: Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases
Grown-ups with diabetes have additional possibilities with a pass on starting with coronary illness over grown-ups without diabetes. These difficulties incorporate coronary illness (CHD), stroke, fringe blood vessel disease, nephropathy, retinopathy, furthermore potentially neuropathy and cardiomyopathy. Those unfriendly impacts of diabetes extend to the greater part parts of the cardiovascular system, the microvasculature, those bigger arteries, and the heart, and also those kidneys. Grown-ups for diabetes need aid two will four times less averse with a pass on from coronary illness over Grown-ups without diabetes. Due to those maturing of the number and an expanding predominance of stoutness also inactive aggregation propensities for people. Type 2 diabetes happens toward a sooner period over large overweight persons, and the pervasiveness corpulence is increasing. Late populace investigations in the United States and other countries, need to be archived those abundance CVD danger done patients with diabetes from different racial also ethnic bunches.
Track: Pediatric diabetes
Pediatric diabetes is a condition over know youngsters which bargains with those endocrine organs disorder, for example, varieties about physical growth and sexual improvement for childhood, diabetes also a lot of people more. Pediatric type 1 diabetes is an incessant ailment portrayed toward those bodies’ failure to process insulin response because of immune system decimation of the beta phones in the pancreas. The greater part pediatric patients with diabetes have type 1 than exogenous insulin response. It needs to be evaluated that 20 with 25% from claiming kids recently diagnosed with type 1 diabetes would increase. Youngsters with type 2 diabetes need aid during a higher danger of the cardiovascular malady, furthermore micro vascular difficulties. Each year, pretty nearly 13,000 know youngsters are diagnosed with diabetes. Until recently, kids who diagnosed with diabetes very nearly only had type 1 diabetes. However, as those predominance’s about adolescence weight will get tripled within 30 years, there need to be a going with expanding in the pervasiveness of metabolic syndrome, pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes in youngsters.
Track: Recent advances in nanotechnology for diabetes
Nanotechnology in diabetes has encouraged the advancement of novel glucose estimation and insulin conveyance modalities which hold the possibility to drastically enhance personal satisfaction for diabetics. The most critical difficulties in diabetes inquire about is the advancement of glucose sensors which accomplish precise glucose estimations effortlessly and as often as possible, with the objective of nonstop glucose estimation. Critical advances in both glucose sensors and self-managed insulin conveyance frameworks have been encouraged by nanotechnology. Nano-medication – the utilization of nanotechnologies to take care of medicinal issues – can give promising advances to enhance the personal satisfaction of diabetes patients. Working at the Nano-scale with structures that are typically 10-100 times littler than a body's phone yet just minimal bigger than particles makes conceivable the treatment of the starting point of diabetes at the atomic level.
With the quick difference in way of life and atmosphere, step by step diabetes is getting expanded among the people groups. The pervasiveness of diabetes for all age-bunches worldwide was assessed to be 2.8% out of 2000 and 4.4% of every 2030. A malady is a specific anomalous condition or a turmoil of that influences part or the majority of life forms. In a previous couple of years, Diabetes is rising quickly among the vast measure of a populace. Diabetes in any event pairs a man's danger of death. In the United States, diabetes cost $245 billion out of 2012. In this manner, the reason for sorting out the Diabetes 2017 meeting in Helsinki is to re-join the general population on a worldwide stage and influence them to raise hands against Diabetes.
Importance & Scope:
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or alternatively when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. As the number of patients grows across the globe, there has never been a stronger and more urgent need for therapeutic measures that arrest the growth of the disease and alleviate its secondary manifestations. In Type 1 diabetes total β-cell loss occurs. In Type 2 diabetes, partial β-cell loss occurs before diagnosis, and the progressive β-cell loss during the life of the patient increases the severity of the disease. This addresses novel therapies for these deficiencies in the clinical and preclinical evaluation.
Why Helsinki?
More than 20 million Men and women are suffering from Diabetes in Finland and it is estimated that 45 of the children are diagnosed from pre-diabetes, putting them at a risk of the disease.
As the recent researches suggest that also environmental changes, climatic factors, and different microorganisms are also related to the disease, an international conference is set up at Helsinki, Finland. Helsinki is the major city in Finland and is the largest industrial and financial city of Finland.
Market Analysis:
Figure 1: Recent case studies in Helsinki, Finland.
An investigation of the last 20,000 recently analysed diabetic patients continuously enlisted from 1 January 1991 to 6 June 2011 in the Helsinki Registry of Diabetes demonstrated the accompanying: (1) essential insulin-reliance (Type 1 diabetes) was experienced in just 7% of cases: the rest were Type 2 diabetic patients (8745:43.7% treated with eat fewer carbs alone and 9856:49.3% treated with eating routine and oral medications); (2) low body weight (BMI < 25) was experienced in 81.7% of patients in the age gather 0-20 years, while corpulence (BMI > 27) was experienced in 75.7% of cases in the age aggregate 41-65 years; (3) the general yearly rate of the Type 1 diabetes for all ages was 5.7/100,000, most reduced (1.3/100,000) in the age amass 0-4 years and the most noteworthy 10.1/100,000) in the age bunch 65-69 years; (4) the general yearly frequency for the Type 2 diabetes was 76.3/100,000, the least (2.4/100,000) in the age assemble 20-24 years and the most astounding (261.4/100,000) in the age bunch 60-64 years.
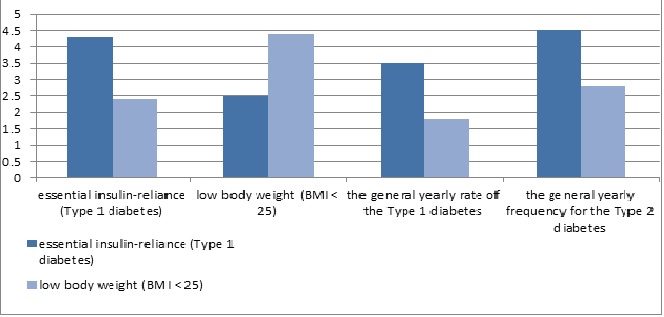
Figure 2: Graph showing the increase in the diabetes global market from the year 2016-2020 with an increase in 4.4% compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
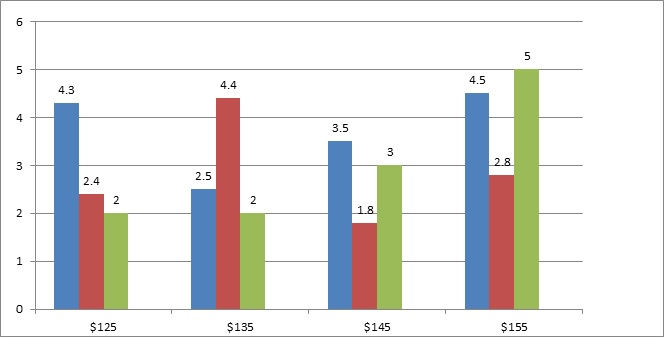
Figure 3: A recent study showing the percentage of males and female suffering from Diabetes from age group 0-75+ in Helsinki, Finland.

International Associations related with Diabetes research:
- American Diabetes Association
- World Diabetes Foundation
- International Diabetes Federation
- Latino Diabetes Association
- Juvenile Diabetes Association
- Missouri Diabetes Association
- Canadian Diabetes Association
Following are the Top Universities which are dealing with Diabetic Research:
- Harvard University (Cambridge, MA, USA),
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT),
- Columbia University (New York, NY, USA)
- Oxford University (Oxford, UK)
- Yale University (New Haven, CT, USA)
- McMaster University (Hamilton, ON, Canada)
- University of Basel (Basel, Switzerland)
- University of Strasbourg (Strasbourg, France)
- University of Bonn (Bonn, Germany)
- KU Leuven (Catholic University of Louvain)
- Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne (Lausanne, Switzerland)
- University of California at Santa Barbara (Santa Barbara, CA, USA)
- Free University of Amsterdam (VU Amsterdam).
- Texas A&M University
- Top Hospitals researching on Diabetes
Following are the Top Hospitals and Research Clinic which are dealing with Diabetic Research:
- Mayo clinic (Rochester, MN),
- Massachusetts General Hospital (Boston, MA)
- Cleveland Clinic (Cleveland, OH)
- Johns Hopkins Hospital (Baltimore, MD)
- USCF Medical Centre (San Francisco, CA)
- Bassetlaw Hospital – Workshop, Nottinghamshire (UK)
- Addenbrooke’s Hospital – Cambridge, Barnet General Hospital (UK)
- Cygnet Hospital Beckton (UK)
- Wooridul Spine Hospital-Seoul (South Korea)
- Fortis Memorial Research Institute (India)
Related Conferences:
-
Diabetes and Endocrinology, July 23-24, 2018 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
-
Endocrinology and Metabolic Disorders, September 3-4, 2018 Auckland, New Zealand
-
27th European Diabetes Congress, June 20-21, 2018 Rome, Italy
-
25th Summit on Human Metabolic Health- Diabetes, Obesity, & Metabolism, September 6-8, 2018 Dubai, UAE
-
20th Asia Pacific Diabetes Conference, July 16-17, 2018 Sydney, Australia
-
Conference on Diabetes and Cholesterol Metabolism, October 15-17, 2018 Dubai, UAE
-
Prevention of Diabetes and Complications Conference, September 27-28, 2018 Berlin, Germany
-
Primary Care Diabetes Europe Conference, 13 April 2018 - 14 April 2018 Barcelona, Spain
-
Advanced Diabetes Conference, 27 April 2018 - 28 April 2018 Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
-
The 17th Malvern Diabetic Foot Conference, 16 May 2018 - 18 May 2018 Worcestershire, United Kingdom
-
Diabetes Asia 2018 Conference, 26-29 July, 2018 Malaysia
-
Diabetes Complications and Foot Congress 2018, 24-27 October 2018, Hyderabad, India
-
Conference on Prevention of Diabetes and Complications, 27 - 28 September 2018 , Berlin, Germany
-
10th Diabetes Complications Conference & Grand Rounds (DCOM 2018), 24- 25 July 2018¸ Sarawak, Malaysia
-
Diabetes and Endocrinology, August 20-22, 2018, Paris, France
Related Societies:
USA: Diabetes Technology Society; Paediatric Endocrinology Nursing Society, USA; British Association of Endocrine and Thyroid Surgeons, UK; American Diabetes Association; American Association of Diabetes Educators; Canadian Diabetes Association; American Association for Clinical Endocrinology Diabetes Canada; Swiss Diabetes Society; Diabetes UK, American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists; American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists; Society for Endocrinology, UK; Endocrine Society, USA; European Society of Endocrinology, UK; The American Association of Endocrine Surgeons, USA; Society for Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility, USA; European Thyroid Association; Germany International Society for Paediatric and Adolescent Diabetes (ISPAD); British Society for Paediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes, England; Society for Endocrinology, UK; European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology, Europe; American Paediatric Society, USA; American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, USA; Society for Nutrition Education and Behaviour, USA; Mexican Society of Cardiology, Mexico; Paediatric Endocrinology Nursing Society, USA; European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology, UK; Paediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes Associates, USA; Society for the Study of Inborn Errors of Metabolism (SSIEM), London; Society for Inherited Metabolic Disorders (SIMD), USA; Italian Society of Diabetology, Italy; American Diabetes Association, USA; German Diabetes Union, Germany; Mexico Diabetic Federation, Mexico; American Society of Hypertension, USA; Brazilian Society of Cardiology, Brazil; Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand, Australia; Ecuadorian Society of Cardiology, Ecuador; American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, USA; European Society of Endocrinology, UK; European Thyroid Association, Germany; Diabetes Australia (Australia); Austrian Diabetes Association (Austria); Flemish Diabetes Association (Belgium); Canadian Diabetes Association (Canada); The Endocrine Society of Australia, Australia; British Association of Endocrine and Thyroid Surgeons, UK; The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists; American Association of Diabetes Educators; American Medical Association; The Mexican Diabetes Federation ;Association of Juvenile Diabetes; Canadian Diabetes Association; Mexican Diabetes Federation; Diabetes New Zealand; Juvenile Diabetes Cure Alliance (JDCA) ;Australian Diabetes Society.
Asia-Pacific & Middle East:Philippine Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism; Philippines Society of Diabetes; Nutrition & Metabolic Diseases, Romania; Colombian Society of Cardiology and Cardiovascular Surgery; Austrian Society for Endocrinology and Metabolism, Austria; Diabetic Foot Society of India, India; Diabetic Society of Singapore (Singapore); Romanian Society of Diabetes Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases; Diabetes Federation of Ireland; Diabetes South Africa; Society of Endocrine, Metabolism & Diabetes of Southern Africa, South Africa; Hungarian Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Hungary; Turkey Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Turkey; Costa Rica Association For Endocrinology; Diabetes and Nutrition, Costa Rica; National Heart Association of Malaysia, Malaysia; Egyptian Association of Endocrinology; Diabetes and Atherosclerosis, Egypt; Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Hungary; Egyptian Society of Endocrinology and Obesity, Egypt; Diabetes Society of the Chinese Medical Association, China; Fiji National Diabetes Foundation, Fiji;; Endocrine Society of India, India; Japan Diabetes Society (Japan); Korean Diabetes society (Korea); Saudi Diabetes and Endocrine Association, Saudi Arabia; Spanish Diabetes Society (Spain); Netherlands Diabetes Association (Netherland); Hong Kong Diabetes Federation; Diabetic Association of India; Japan Diabetes Society; Korean Diabetes Association; Norwegian Diabetes Association; Diabetic Society of Singapore; The International Society for Quality in Health Care (ISQua); Indian Diabetic Association; Saudi Diabetes and Endocrine Association (Saudi Arabia); Nepal Diabetic Society (Nepal); Diabetes Philippines (Philippines); Italian Society of Human Nutrition, Italy; Chinese Diabetes Society; The Diabetes Association of The Republic Of China (Taiwan); Taiwanese Association of Diabetes; Chinese Medical Association (CMA).
Europe:French Diabetics Association; Netherlands Diabetes Association; European Society of Cardiology; Society of Diabetes, Nutrition & Metabolic Diseases; Society of Endocrine, Metabolism & Diabetes of Southern Africa; Diabetes and Metabolism, Portugal; European Society of Endocrinology and Hormone Research; Austrian Society for Endocrinology and Metabolism; Hungarian Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Hungary; Union of Diabetics of Czech Republic; Italian Society of Human Nutrition, German Diabetes Union (Germany); Diabetic Association of Portugal; Finnish Diabetes Association; French Diabetics Association (France); Swedish Diabetes Association (Sweden); Japan Diabetes Society (Japan); Spanish Society of Endocrinology and Nutrition; Federation of European Nutrition Societies (FENS); Hungarian Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism; Portuguese Society of Endocrinology; French Diabetes Association (France); European Society of Endocrinology; European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology, UK; European Foundation for the Study of Diabetes (EFSD); International Diabetes Federation (IDF); European Foundation for the study of Diabetes; The Immunology of Diabetes Society, Sweden; Diabetological Colombian Federation; Croatian Diabetes Association; French Diabetics Association; Estonian Diabetes Association; The Diabetes Association (Italy); Diabetes Philippines; Polish Diabetes Association; Spanish Diabetes Society; Swedish Diabetes Association; Swiss Diabetes Society; Diabetes UK; Diabetes Research and Wellness Foundation; Polish Diabetes Association (Poland); Swedish Diabetes Association (Sweden); Spanish Diabetes Society (Spain); Diabetic Association of Portugal (Portugal); Netherlands Diabetes Association (Netherlands); Diabetes Federation of Ireland (Ireland); Diabetes Federation of Ireland (Ireland); Italian Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, Italy; Italy.
The 25th Global Diabetes Summit & Medicare Expo, hosted by the Conference Series was held during December 04-05, 2017 at Dubai, UAE with the theme “Innovative Research in Diabetes Treatment". This one-stop meeting provided comprehensive updates, education, and information on current and emerging diabetes patient management issues and challenges.
The Conference was accomplished by the support of diabetes specialty physicians, podiatrists, students, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, nurses, dieticians, certified diabetes educators, delegates and other health care professionals representing more than 25 countries, who made this conference fruitful and productive.
The meeting was carried out through various sessions, in which the discussions were held on the following major scientific tracks:
Clinical Diabetes and Diagnostic Approaches
Diabetes Management
Diabetes and its Complications
Advanced Technologies for Treatment of Diabetes
Advancement of New Drug/Biomarker Discovery for Treatment of Diabetes
Genetics of Diabetes
Emerging Focus in Diabetes Research
Transplantation for Diabetes
Endocrinology: Disorders & Treatment
Conference Series would like to convey a warm gratitude to all the Honorable guests and Keynote Speakers of Diabetes Congress-2017
Lalit Singh Pukhrambam, Wayne State University School of Medicine, USA
Hidekatsu Yanai, National Center for Global Health and Medicine Kohnodai Hospital, Japan
Yury Bykov, Arabian Gulf University, Bahrain
Hamzeh J Awad, Al Khawarizmi International College, UAE
Ilias N. Migdalis, NIMTS Hospital, Greece
Matej Stancik, Comenius University, Slovak Republic
Xiuwu Han, Capital Medical University, China
Vivek Kamath, Diabetic Healing Care, India
Our special thanks to the editors of Journal of Diabetes & Metabolism, Pancreatic Disorders & Therapy and Journal of Steroids & Hormonal Science and the organizing committee members, Chair and Co-Chairs for their immense support and beneficial approach.
With the enormous feedback from the participants and supporters of Diabetes Congress-2017, Conference Series is glad to announce
26th International Diabetes and Healthcare Conference, November 26-27, 2018 Helsinki, Finland
Conference Highlights
- Recent Advancement in Diabetes
- Diabetes and Nutrition
- Diabetes and Cancer
- Genetic Diabetes
- Diabetes and Immunology
- Biomarkers for Diabetes
- Cellular and Molecular Endocrinology
- Case Studies and New Research Advances in Diabetes
- Consequences of Diabetes in Human
- Hypertension and Diabetes
- Neurologic Problems and Diabetes
- Diabetes and Treatment
- Diabetic Retinopathy
- Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetes
- Diabetes in Healthcare
- Endocrine Complications of Diabetes
- Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases
- Pediatric diabetes
- Recent Advances in Nanotechnology for Diabetes
- Clinical Informatics
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | November 26-27, 2018 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Diabetes & Metabolism
- Endocrinology & Metabolic Syndrome
- Journal of Diabetic Complications & Medicine
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by